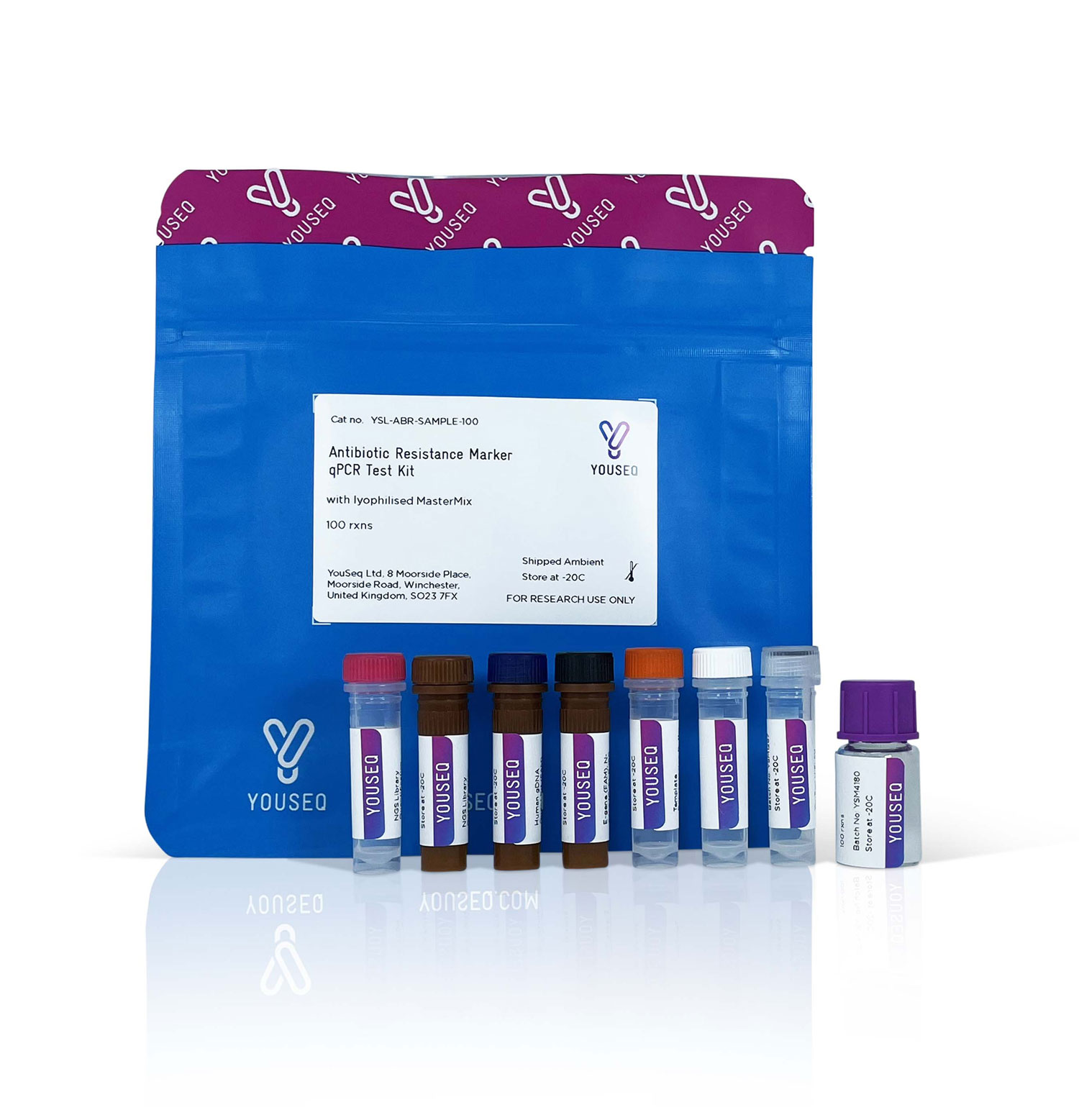
A complete qPCR kit for the detection of Sulfonamides (Sul1) Resistance
Sulfonamides (Sul1) resistance is a major concern in the health sector, especially in both human and veterinary medicine. It is a marker for antibiotic resistance, impacting the treatment of bacterial infections caused by various pathogens. Failure to detect Sul1 resistance early can lead to treatment failure, increased healthcare costs, and the spread of resistant strains within populations.
YouSeq's qPCR kit to detect Sul1 resistance allows for sensitive and specific detection of this important marker. Early detection of Sul1 resistance can help healthcare providers prescribe appropriate antibiotics, reduce the spread of resistant bacteria, and ultimately improve patient outcomes. By using YouSeq's qPCR kit, users can quickly and accurately identify Sul1 resistance, leading to better treatment decisions and overall health outcomes.

Price on enquiry
Order nowFor Research Use Only. Not intended for diagnostic use.
Contents
Endogenous control primer/probe
qPCR MasterMix
Positive control template
DNase/RNase free water
Template resuspension buffer
ROX passive reference
Technical specification
Efficiency: 90-110%
Run Time: Approx 1hr30 (dependent on instrumentation)
Target Marker: FAM labelled
Endogenous Control: VIC/HEX labelled
Product variants
YS-ABR-Sul1-100 : Frozen version for dry ice shipping
Pseudonyms
Escherichia coli; E. coli; Salmonella enterica; S. enterica; Staphylococcus aureus; S. aureus; Klebsiella pneumoniae; K. pneumoniae; Shigella; Enterobacter; Proteus mirabilis; P. mirabilis; Clostridium difficile; C. difficile; Streptococcus pneumoniae; S. pneumoniae; Haemophilus influenzae; H. influenzae; Neisseria gonorrhoeae; N. gonorrhoeae; Pseudomonas aeruginosa; P. aeruginosa; Acinetobacter baumannii; A. baumannii; Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus; MRSA; Vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus; VRE; Extended-spectrum beta-lactamase-producing bacteria; ESBLs; Multidrug-resistant bacteria; MDR bacteria; Hospital-acquired infections; HAIs; Community-acquired infections; CAIs