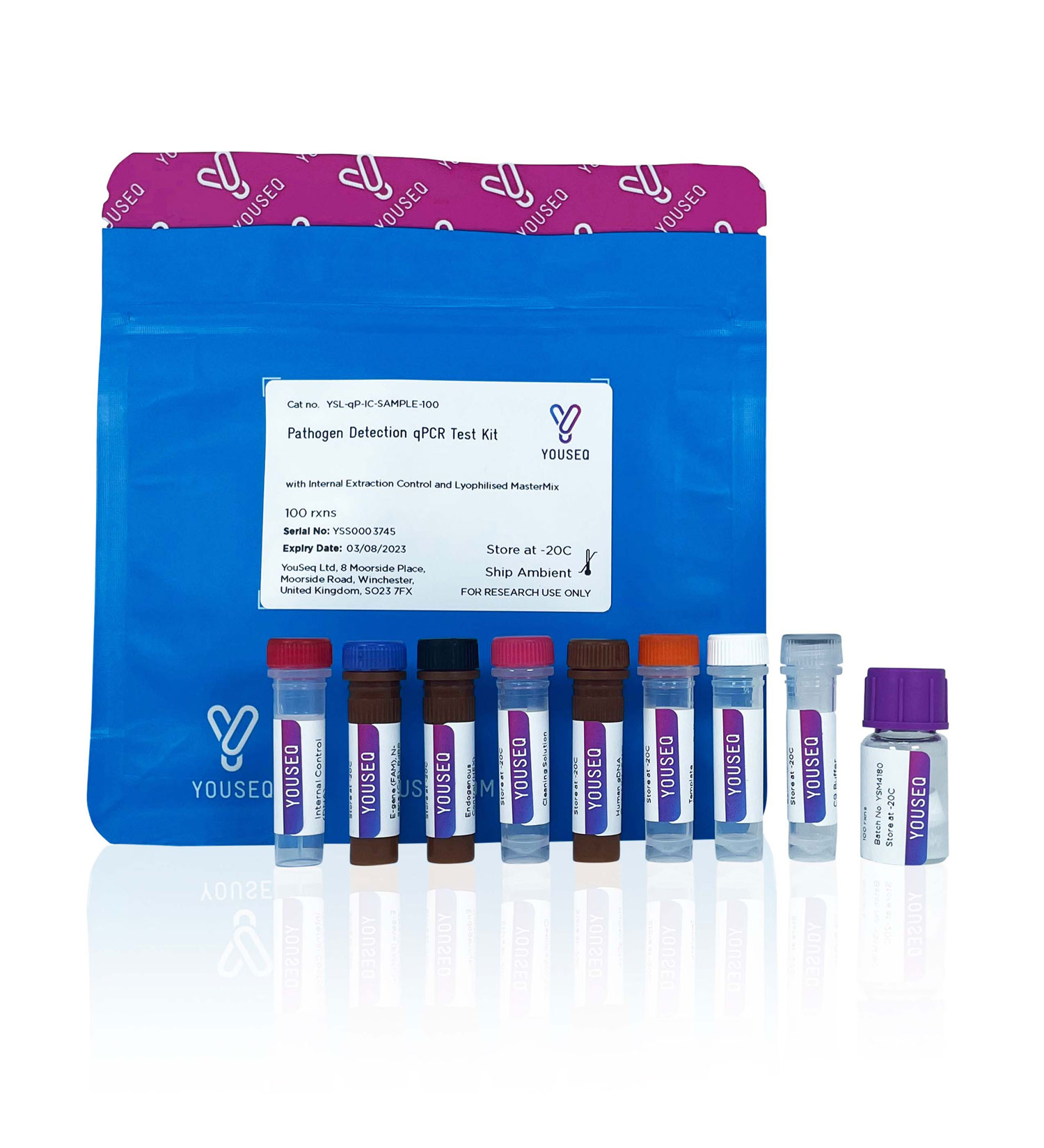
A complete qPCR kit for the detection of Canine adenovirus type 1
Canine Adenovirus Type 1 (CAV-1) is a highly contagious virus that primarily affects dogs, causing symptoms such as coughing, fever, and respiratory distress. It is important to detect CAV-1 early in veterinary settings to prevent the spread of the virus and ensure the health and well-being of animals in the veterinary sector.
YouSeq's qPCR kit to detect Canine Adenovirus Type 1 allows for quick and accurate identification of the virus, helping veterinarians to implement timely treatment and prevent further transmission. Early detection of CAV-1 can significantly impact the overall health and safety of animals in veterinary care, leading to better outcomes and reduced spread of the virus within the canine population.

Price on enquiry
Order nowFor Research Use Only. Not intended for diagnostic use.
Contents
Internal extraction control primer/probe
qPCR MasterMix
Positive control template
DNase/RNase free water
Template resuspension buffer
Internal extraction control (DNA)
ROX passive reference
Technical specification
Efficiency: 90-110%
Sensitivity: <100 copy detection
Run Time: Approx 1hr30 (dependent on instrumentation)
Target Pathogen: FAM labelled
Internal Control: VIC/HEX labelled
Product variants
YS-qP-IC-CAdV1-100 : Frozen version for dry ice shipping
Pseudonyms
Canine adenovirus type 1; Infectious canine hepatitis virus; CAV-1; Rubarth disease virus; Canine adenovirus 1