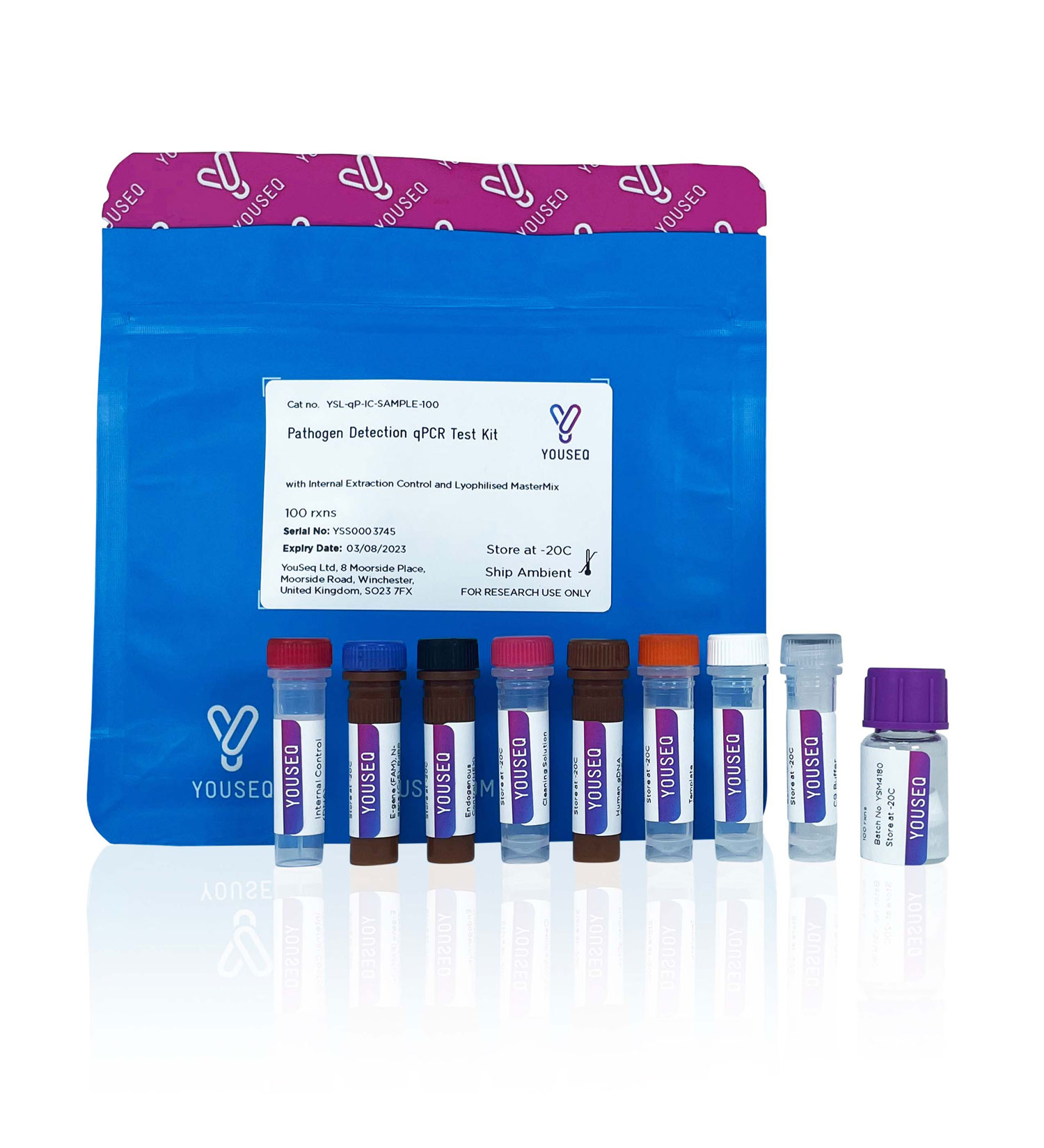
A complete qPCR kit for the detection of Brucella SPP
BRUCELLA SPP: Brucellosis, also known as Malta fever or Mediterranean fever, is a zoonotic disease caused by Brucella spp. It can affect both humans and animals, leading to flu-like symptoms such as fever, joint pain, and fatigue. This pathogen is important to detect in the veterinary and human health sectors to prevent the spread of the disease and potential outbreaks.
YouSeq's qPCR kit to detect Brucella spp allows for sensitive and specific detection of this pathogen, enabling early diagnosis and treatment. Early detection of Brucella spp is crucial in preventing the transmission of the disease to humans, reducing the economic burden on agriculture, and ensuring public health safety.

Price on enquiry
Order nowFor Research Use Only. Not intended for diagnostic use.
Contents
Internal extraction control primer/probe
qPCR MasterMix
Positive control template
DNase/RNase free water
Template resuspension buffer
Internal extraction control (DNA)
ROX passive reference
Technical specification
Efficiency: 90-110%
Sensitivity: <100 copy detection
Run Time: Approx 1hr30 (dependent on instrumentation)
Target Pathogen: FAM labelled
Internal Control: VIC/HEX labelled
Product variants
YS-qP-IC-Bruce.SPP-100 : Frozen version for dry ice shipping
Pseudonyms
Brucella spp; Brucellosis; Bang's disease; Undulant fever; Mediterranean fever; Malta fever; Gibraltar fever; Rock fever; Cytochrome c oxidase pathogen